Artery Forceps Uses & Types
Artery Forceps Uses & Types
Introduction to Artery Forceps
Overview
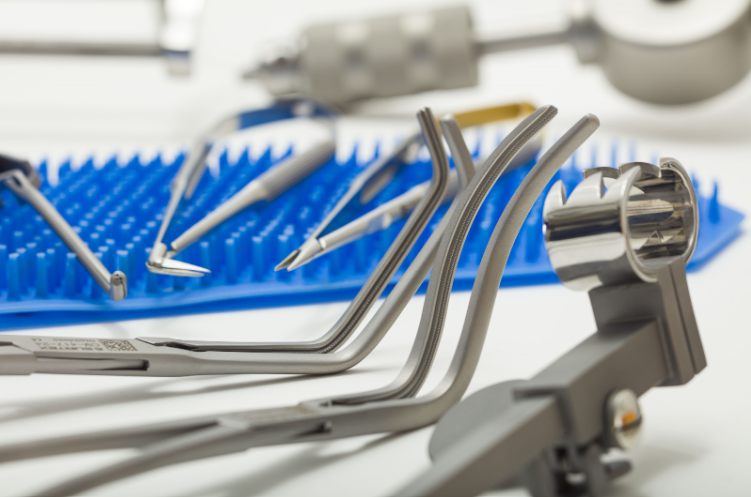
Artery forceps are vital surgical instruments used to control blood flow during various medical procedures. They come in different types, shapes, and sizes, each designed for specific applications. We will explore the general types, features, and functions of artery forceps.
Types of Artery Forceps
The following table illustrates the common types of artery forceps and their general uses:
| Type | General Use |
|---|---|
| Straight Artery Forceps | Clamping large blood vessels, manipulating tissues |
| Curved Artery Forceps | Clamping vessels in deep spaces |
| Long Artery Forceps | Reaching into deep surgical sites |
| Small Artery Forceps | Delicate procedures in confined areas |
There are straight artery forceps with smooth jaws for clamping blood vessels and tissues gently. The straight design allows for easy access in open surgical sites.
Curved artery forceps have angled jaws to clamp arteries and tissues in hard-to-reach areas like deep body cavities. The curved jaws provide better visibility and control.
Long artery forceps have extended shafts to access blood vessels deep within surgical sites. The extra length enables surgeons to reach deep into body cavities and spaces.
Small artery forceps have fine, pointed jaws for precision work in confined spaces like neurological or vascular procedures. The delicate jaws allow controlled clamping of tiny blood vessels.
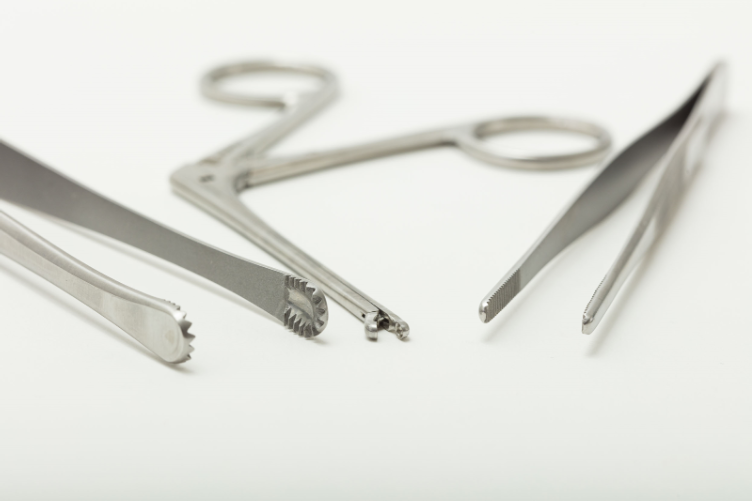
Features and Parts of Artery Forceps
Artery forceps consist of several key components, each serving a specific function:
- Ratchet: A locking mechanism that secures the jaws in a closed position to maintain constant pressure on clamped blood vessels. This allows hands-free clamping.
- Jaws: The working end of the forceps that clamps down on tissues or blood vessels. Jaws can be straight or curved, smooth or serrated.
- Handles: Ergonomically designed grip handles for comfort and control when clamping. Spring handles provide tension.
- Shaft: Connects the jaws to the handles. Varies in length depending on type – long, medium or short. Allows access into deep spaces.
- Lock: A catch or notch that keeps the jaws closed when ratcheted. Releases when handles are compressed.
- Teeth: Serrated jaws have small teeth to grip slippery tissues and vessels securely. Smooth jaws are less traumatic.
- Tips: Fine tips allow precise dissection and manipulation of delicate vessels and tissues.
Indications and Sterilization
Artery forceps are indicated for a broad range of surgical specialties, including:
- Cardiovascular surgery
- Orthopedic surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Plastic surgery
- General surgery
- Obstetrics and gynecology
- Urological procedures
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
Proper cleaning, disinfection and sterilization are essential to maintain the integrity and safety of artery forceps. Most models are made of high-grade stainless steel and can withstand steam autoclaving, dry heat sterilization, and various liquid disinfecting solutions.
Specific Models and Their Applications
Section 2
In this section, we will delve into specific models of artery forceps available and their specialized uses for different surgical procedures. Meticulous handcrafting and quality control ensure the instruments meet high manufacturing standards.
Specific Models and Their Uses
The following table highlights some common artery forceps models and their particular applications:
| Model | Specialized Use |
|---|---|
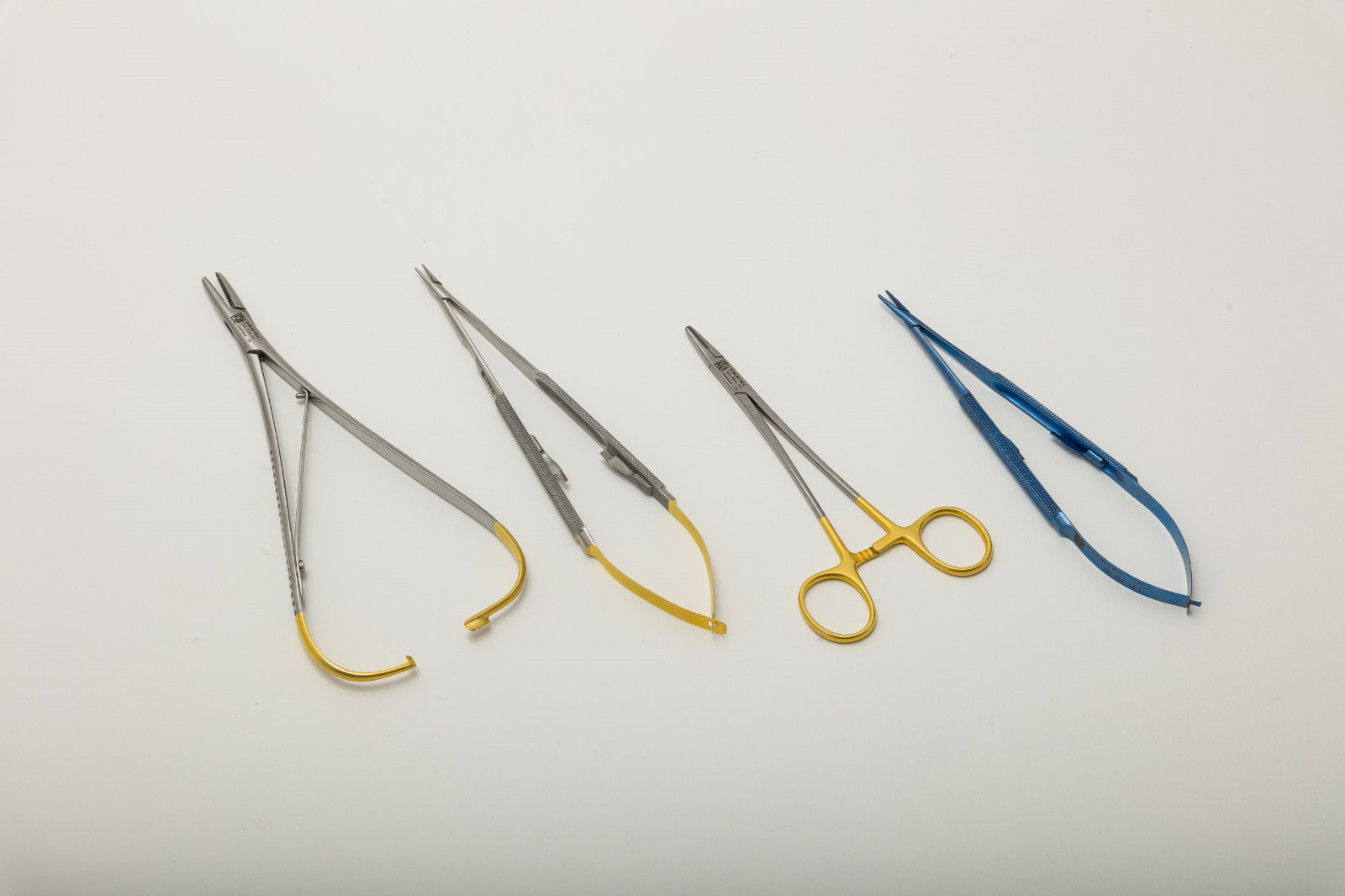
| Adson Artery Forceps | Holding and manipulating delicate tissues |
| Allis Tissue Forceps | Grasping soft tissues |
| Babcock Intestinal Forceps | Handling bowel, appendix, ovary |
| Crile Artery Forceps | Clamping vessels in deep areas |
| Micro Mosquito Artery Forceps | Microsurgery, spinal, ENT procedures |
| Kelly Artery Forceps | Cardiovascular, Dental, ENT, General Surgery, Gynecology & Obstetrics, Neurosurgery / Spine, Oral & Maxillofacial, Orthopedic, Stomach, Intestine & Rectum, Urology, |
| Kocher Artery Forceps | Clamping large arteries, tissues |
| Pean Artery Forceps | General surgery, clamping vessels |
| Rochester-Carmalt Forceps | Delicate clamping, fiber dissection |
| Spencer Wells Artery Forceps | Vascular and thyroid procedures |
Adson artery forceps have fine tips for delicate handling of vessels and soft tissues, especially in confined spaces like the eyes or under flaps. The small size provides precision grasping.
Allis tissue forceps securely grasp soft body tissues with serrated jaws. The locking mechanism keeps a firm hold during manipulation and dissection. Useful in abdominal, orthopedic and OB-GYN surgeries.
Babcock intestinal forceps have angled jaws to gently handle friable bowel tissue and appendices during open and laparoscopic procedures. The atraumatic design reduces risk of damage.
Crile hemostatic forceps allow clamping and compressing of vessels and tissues in deep surgical sites thanks to the curved jaws and long shaft. Ideal for vascular procedures.
Halstead mosquito forceps have very fine, curved jaws for microsurgery like ophthalmology or neurosurgery. The delicate design provides precision grasping of miniature vessels and nerves.
Kelly hemostatic forceps are designed specifically for obstetrics, gynecology and urologic procedures like cystoscopy. The angled jaws provide better access and visibility.
Kocher artery forceps can securely clamp even large arteries thanks to the strong ratchet lock and curved, toothed jaws. Invaluable in open and laparoscopic surgeries.
Pean artery forceps are general purpose forceps with either straight or curved jaws. The serrated teeth provide a firm grasp of vessels while the ratchet lock enables hands-free clamping.
Rochester-Carmalt forceps allow extremely gentle handling of delicate tissues like nerves. The ultra-fine serrations on the jaws offer precise grasping and dissection.
Spencer Wells artery forceps have long, curved jaws to reach blood vessels in deep body sites. Useful for vascular surgery and thyroid procedures. The locking mechanism provides secure hemostasis.
Conclusion
In summary, artery forceps are indispensable surgical tools with many types and models designed for specific applications. Quality craftsmanship and manufacturing processes ensure reliable instruments that meet surgeons’ needs during diverse procedures. With the proper selection and handling, artery forceps can significantly enhance surgical efficiency, safety and patient outcomes.
Join our newsletter
Specify the advantages, benefits of joining the newsletter, setting the spam rate.