Ear Microsurgery Set
The ear consists of three consecutive cavities from outside to inside, that are responsible for the sense of hearing. The outermost cavity is the external auditory canal, which is an air-filled tube that conducts the sound vibrations from the outer ear pinna to the ear drum. The middle ear cavity contains three intricate and articulating bones known as the auditory ossicles, which are the malleus, incus, and stapes (hammer, anvil, and stirrup). It also features a canal known as the Eustachian tube, which connects the middle ear with the nasal cavity and helps to equalize the pressure around the ear drum.
The stapes or the stirrup is the smallest bone in the body, and has a foot that is attached to a membrane known as the oval window. This oval membrane conducts the vibrations of the middle ear ossicles to the inner ear vestibule. The ossicles help amplify the sound vibrations to the inner ear’s cochlea, which transmits the auditory information via the eighth cranial nerve to the brain’s auditory cortex.
Damage to any component in this continuum of structures, from the tympanic membrane to the foot of the stapes, can lead to hearing defects and may require surgical intervention.
The tympanic membrane consists of three layers of thin tissues. Perforation of the ear drum due to trauma or infection damages the integrity of the tissues, and affects the ear drum’s function in transmitting sound. This may also occur in condition known as tympanosclerosis, which leads to fibrosis and thickening of the ear drum. Otosclerosis is the development of pathological firm tissue in the middle ear that prevents the ossicles from conducting sound properly. Inflammations of the middle ear cavity can also lead to fluid building up in the middle ear, and this condition, known as otitis media, is associated with hearing loss, ear pain and fever.
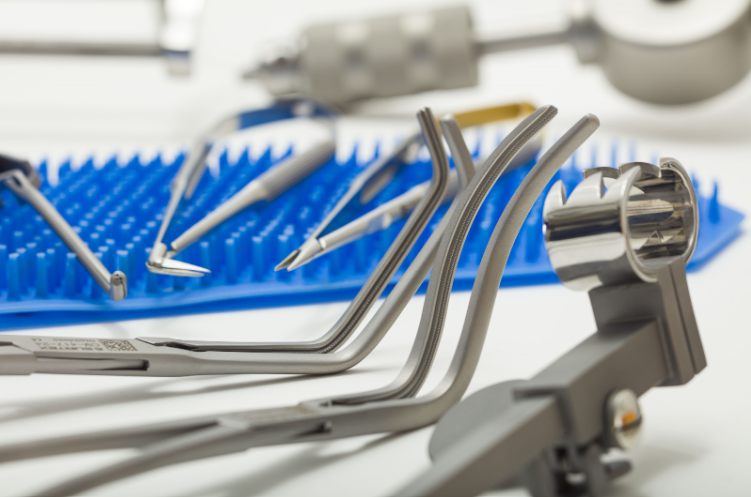
Tympanoplasty may be needed to reconstruct the eardrum or the small bones of the middle ear in such cases of conductive hearing loss. Grafting of the ear drum may be needed, and this requires taking thin layers of tissue from the tragus or temporalis fascia.This procedure may also be accompanied with the exploration of the mastoid bone, especially in cases of mastoiditis that can result from untreated otitis media. Any of several types of tympanoplasty can be performed depending on the extent of the ear drum and ossicular damage. In these procedures, the surgeon may require a microscope to properly view the small ear structures and grafts. This operation also requires microsurgical instruments with small blades that can reliably grasp and mobilize delicate tissues and ultra-fine materials. Micro-Hooks with relatively small and angled blades are also needed to extract and remove scarred or pathological tissues.
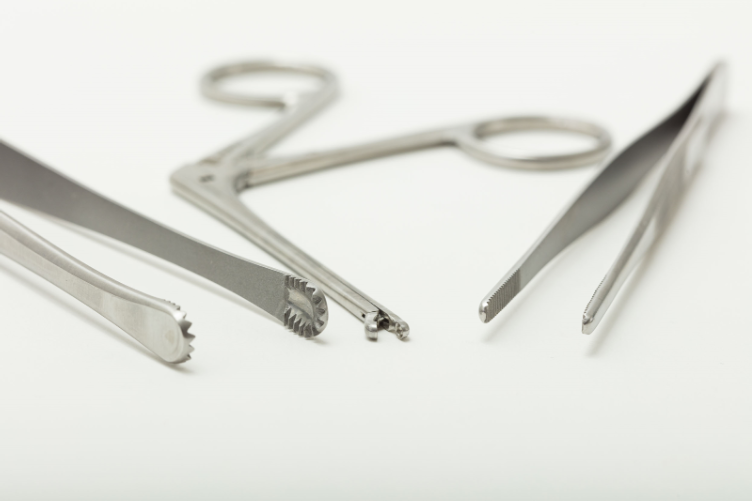
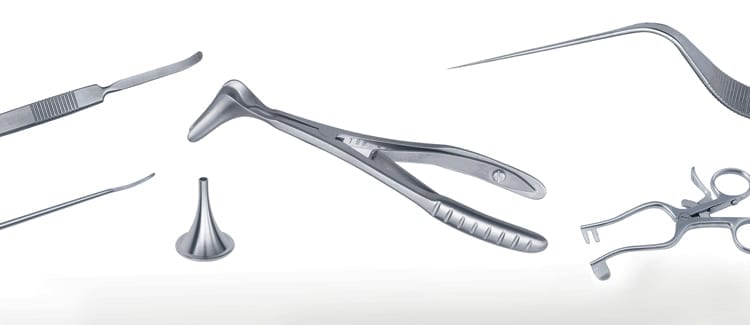
Surtex Instruments manufacture the ear microsurgery set to deliver the best results in these delicate manipulations. This includes a wide variety of self-retaining retractors, such as the Plester Self Retaining Retractor, and ear specula, such as the Hartmann Ear Specula, to open and maintain the surgical field. Hemostatic forceps, such as the straight Rochester-Pean Haemostatic Forcep, are also available to decrease bleeding and maintain clarity. Several figures of micro ear needles are included. These tools are used to perform different and gentle manipulations like freshening the margins of ear drum perforations. Barbara needles with tips that are angled at 25°, 45°, 90° or are curved down, are also available to accommodate different anatomical and surgical indications.
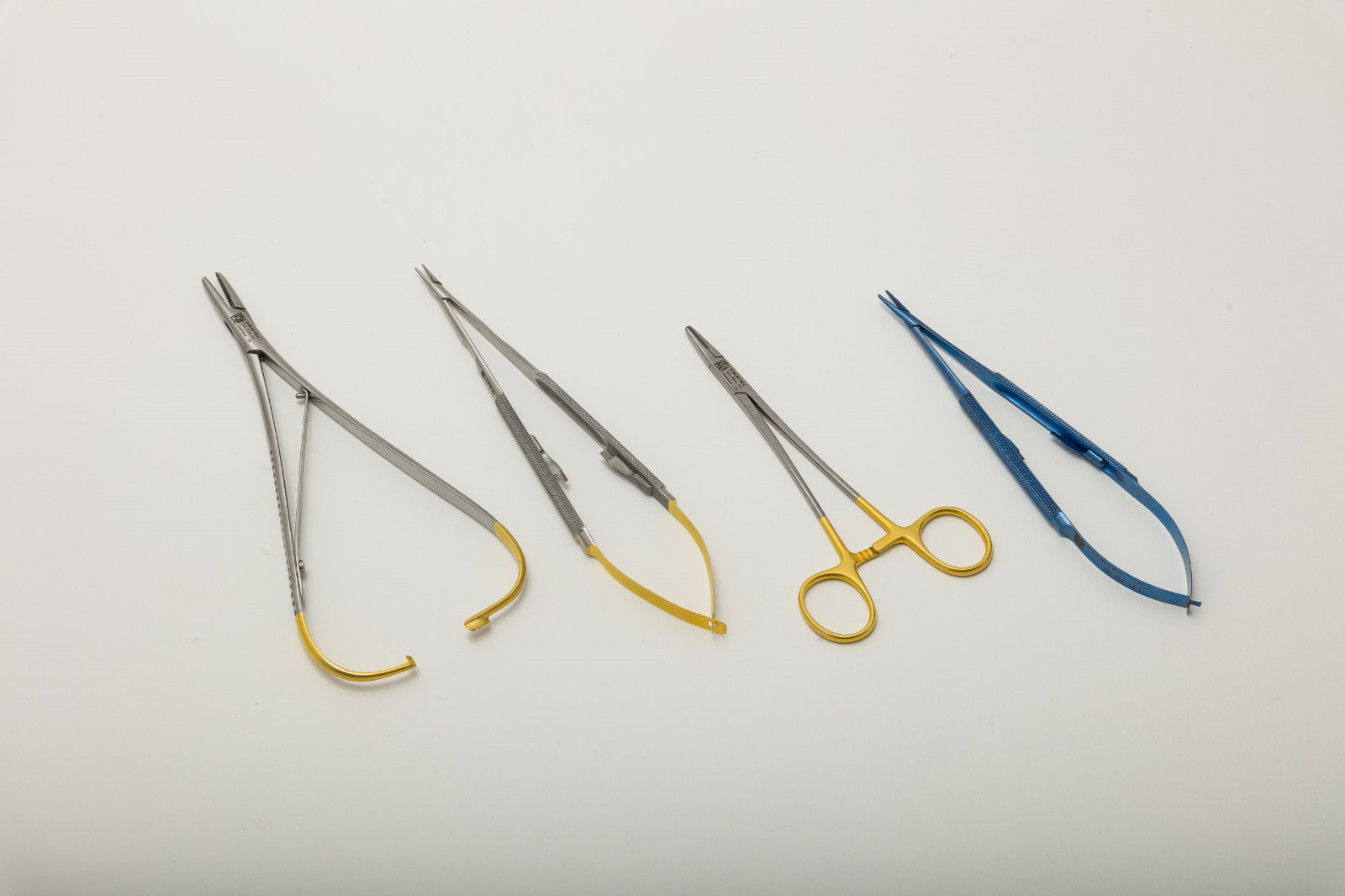
Bellucci Micro Scissors are fine-cutting scissors that can deliver optimal cuts of vital and fragile structures such as the tympanic membrane, minute muscles like the tensor tympani and the stapedius, or nerves such as the chorda tympani. The scissors have dexterous finger ring handles and a prolonged shaft to reach anatomically narrow sites. The Plester Flap Knive is another important instrument in procedures in myringoplasty, tympanoplasty and ossiculoplasty to mobilize tympanomeatal flaps. The McGee Micro Ear Needle is specialized for stapedectomy procedures, to excise pieces of broken footplate and reshape tympanic perforations before placing grafts.
The Rosen Circular Cut Knife is another superior instrument that is designed to raise ear canal skin flaps during tympanoplasty procedures. The advantage of using this knife is that it causes minimal bleeding because it has a duller blade and crushes the blood vessels more firmly. Wullstein Sickle Knives are used to cut through mucosa, freshen eardrum perforations, remove adhesions and excise tendons like that of the stapedius muscle.
Join our newsletter
Specify the advantages, benefits of joining the newsletter, setting the spam rate.