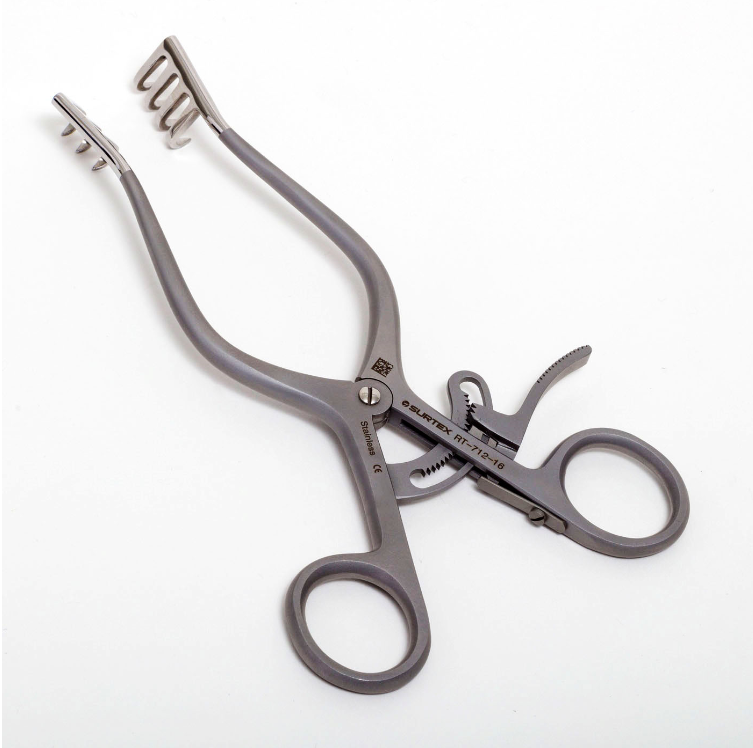
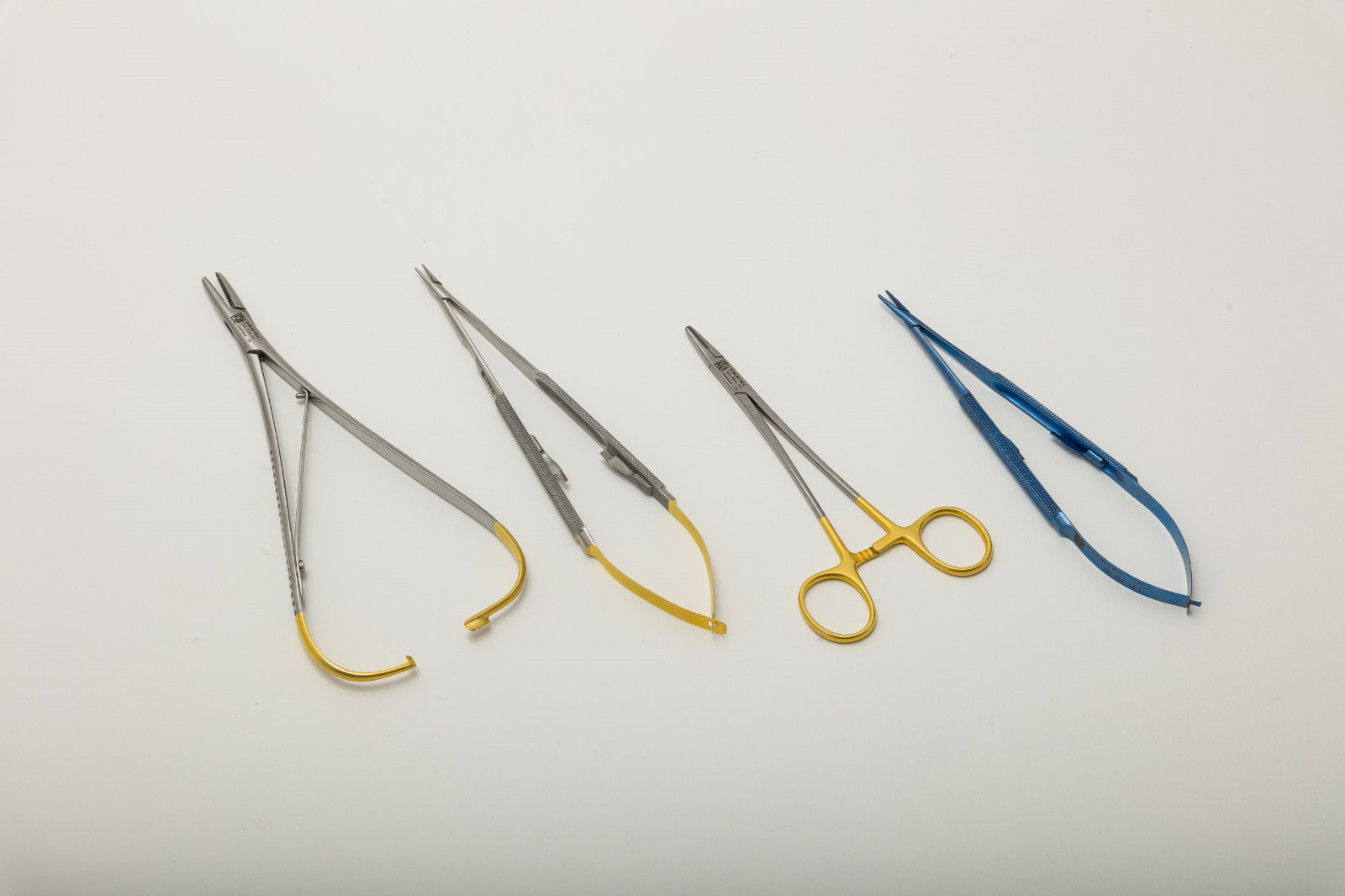
Middle Ear Set
The middle ear is a six-sided box with that is bounded laterally by the tympanic membrane and medially by the labyrinth of the inner ear. It is connected to the nasal cavity by the Eustachian tube, and contains the auditory ossicles. The roof separates it from the cranial cavity, the floor separates it from the jugular bulb, the anterior wall separates it from the internal carotid artery, and the posterior wall lies close to the mastoid air cells. The upper and outer part of the middle ear is known as the attic, and it communicates with a large, air-containing space in the upper part of mastoid, known as the mastoid antrum.
The function of the middle ear is conducting the sound vibrations from the tympanic membrane, through the auditory ossicles (malleus, incus and stapes), to the oval window and the inner ear’s cochlea. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear with the nasal cavity and helps to equalize the pressure around the ear drum.
Damage to the structures conducting sound, from the tympanic membrane to the foot of the stapes, can lead to hearing defects and may require surgical intervention. This includes conditions such as acute suppurative otitis media, which is an acute inflammation of the middle ear by pyogenic organisms. If this condition is not treated properly by antibacterials, a surgical procedure known as myringotomy may be needed. It involves incising the drum to remove the fluid surgically and evacuate the pus.
Severe acute necrotizing otitis media may damage the whole tympanic membrane and require a procedure known as tympanoplasty. Affection of the mastoid air cells in long standing otitis media may require cortical mastoidectomy. Cases of otitis media with non-purulent effusion may also require myringotomy, especially when the fluid is thick and medical treatment does not help. If the condition recurs after myringotomy, a grommet tube maybe inserted to provide sustained aeration of the middle ear. The tube can be left in place for weeks or months or until it is spontaneously extruded.
Myringotomy may also be performed for cases of otitic barotrauma, which occurs when the eustachian tube fails to maintain middle ear pressure at during rapid descent of air flights or in underwater diving. Alternatively, catheterization or politzerization can be used to restore middle ear aeration.
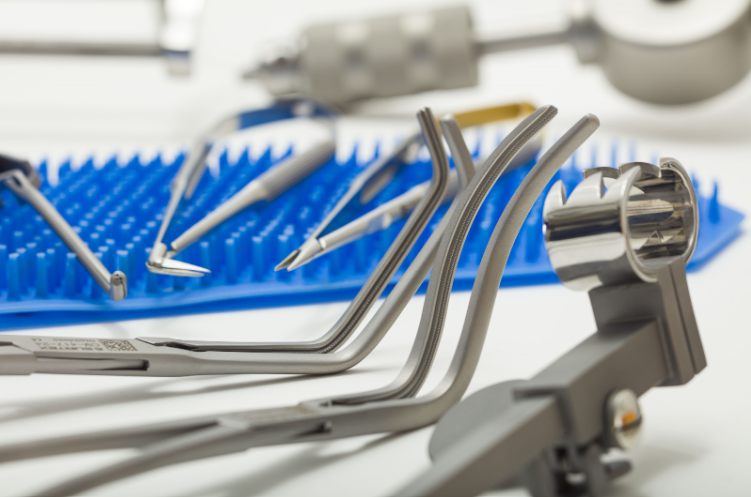
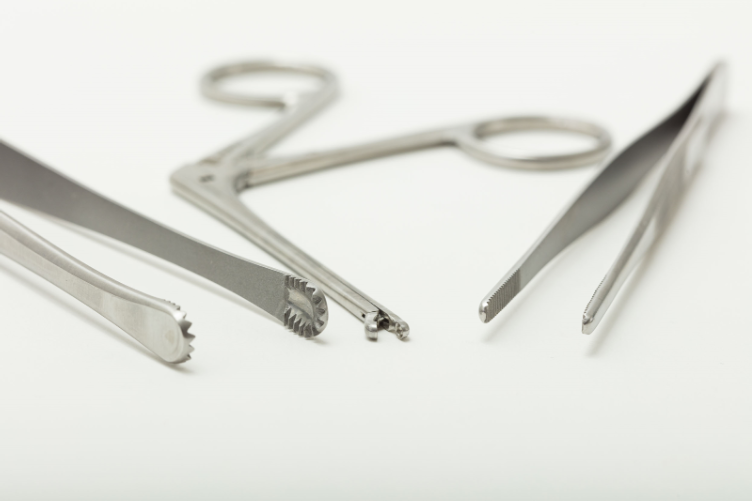
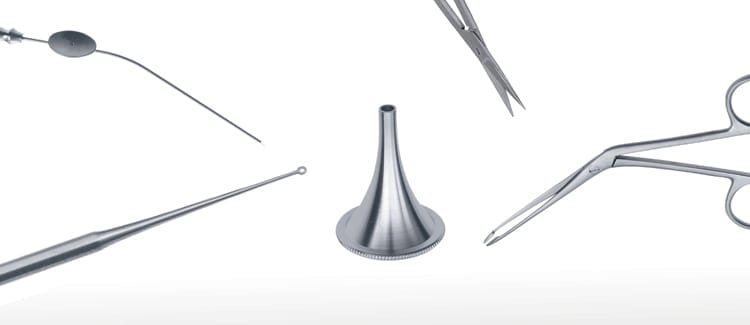
Surtex Instruments manufacture the Middle Ear Set with a wide range of instruments to perform these procedures with superior results. Farrior Ear Specula are cone-shaped tools that are attached to otoscopes to allow the focused inspection of the external auditory meatus and the ear drum. The speculum has a blunt atraumatic tip, and is covered with a black coating to avoid the glare caused by the reflection of light from the otoscope.
Upon dilating the ear canal, thick ear wax may obscure the operator’s vision and decrease their precision. This ear wax, or cerumen, can be removed using the suitable size and shape of curette from our diverse selection of Buck Ear Curettes. Two sizes of Frazier Suction Tubes and three sizes of Baron-Schuknecht Suction Tube are available to be used in cleaning procedures. The suction allows for quick and easy removal of excess amounts of cerumen and thick fluid in otitis media.
This set offer instruments that can serve to deliver precise cutting action includes fine scissors such as the curved Mayo Dissecting Scissor, the straight and curved Strabismus Scissor, as well as the reinforced UltraCut™ TC Metzenbaum-Fine Dissecting Scissor. The Rosen Circular Cut Knife is another superior instrument that is designed to raise ear canal skin flaps during tympanoplasty procedures. It decreases bleeding because it crushes the blood vessels firmly with its blunt blades. Wullstein Sickle Knives are used to cut through mucosa, freshen eardrum perforations, remove adhesions and excise tendons like that of the stapedius muscle. Bellucci Micro Scissors can deliver optimal cuts of vital and fragile structures such as the tympanic membrane, minute muscles like the tensor tympani and the stapedius, or nerves such as the chorda tympani. House-Dieter Malleus Nippers are used to trim the head of the malleus and parts of the incus. The House Micro Ear Curette is a double-ended surgical instrument used to excise bone fragments in mastoid surgery, stapedotomy, facial nerve decompression and tympanoplasty. Langenbeck retractors are used to retract soft tissues and wound edges in order to enhance the visualization of deep structures in mastoid procedures.
Join our newsletter
Specify the advantages, benefits of joining the newsletter, setting the spam rate.